Climate Change Conference 2023
About Conference
Euroscicon generously invites you all to attend the “9th international summit on environmental science & climate change” held during November 21-22, 2023 at Dubai, UAE. This is an astonishing platform for global scientists sharing the information and ability from both scientific and industrial groups as well as the importance of environmental impact assessment. It will impact an attractive moment to meet and interact with professionals in the environment science research field and therefore it takes a delight in opening a way to meet young researchers and speakers where they can show their research and contributions in the field of environmental science and technology, earth science and climatic changes.
The Environmental Science and Climate change 2023 Conference will provide a perfect platform for:
- A Global network with 50+ countries.
- A pre-requisite platform Sponsors & exhibitors
- Explicit talks by the eminent scientists of the global scientific community.
- Sterling workshop sessions.
- Global Recognition to meritorious Researchers
- Novel Techniques benefiting your research
- Global Business and Networking Opportunities
We are sure that Environmental Science and Climate change 2023 will be an outstanding platform for the global scientists to express their ideas and add a vision for their future researchers and prompts collaboration among researchers taking an interest.
Importance & Scope:
Environmental Science involves an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates various academic fields (particularly sciences). Environmental science is important to save our world from destruction. It will create awareness to help social groups and individuals acquire awareness and sensitivity towards the environment as a whole and issues, questions and problems related to environment and development.
The environment studies enlighten us, about the importance of protection and conservation of our indiscriminate release of pollution into the environment.
- It can be significant for the following reasons:
- Environment Issues Being of International Importance
- Problems Cropped in the Wake of Development
- Explosively Increase in Pollution
- Need for an Alternative Solution
- Need To Save Humanity from Extinction
- Need For Wise Planning of Development
Target Audience:
Directors, Managers & Business Delegates, Founders, Universities Faculty, Industries, Investigators, Environmentalists, Post-Doctoral Fellows, Clinical Fellows, Research Scholars, Students, Technology Experts, Environmental Research Companies, Vendors will have the opportunity to introduce the latest advancements in Environmental science to a diverse audience by becoming a conference sponsor via exhibits or workshops
Reasons to Attend the Conference:
- Conference provides the educational opportunities to the students.
- Networking with peers, grow your professional network.
- Expand Your Resources, build your knowledge
Session/Tracks
1. Environmental Science & Technology
Physical, biological, and information sciences are all combined in the academic discipline of environmental science to research the environment. Geography, economics, and political science are some of the social science disciplines that are interwoven into environmental science. The humanities' two disciplines that are also a part of environmental science are philosophy and ethics. Interactions between the deep Earth, the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, and the biosphere control the Earth's surface environment. The periods during which this interaction takes place range from the picoseconds required for chemical reactions on mineral surfaces to the millions of years required for plate tectonics and earth's evolution. In order to comprehend how Earth's geology, climate, and other factors interact, research is ongoing into what factors influence our globe and the ecosystem in which we exist.
- Meteorology
- Hydrology
- Geophysics
- Atmospheric physics
- Physical oceanography
- Advances in biological, physical and chemical processes
- On site and small-scale systems
- Storm-water management
- Emission sources
- Atmospheric modelling and numerical prediction
- Interaction between pollutants
- Aesthetic quality of drinking water (taste, odors)
2. Climate Prediction
Climate prediction is like numerical weather prediction, yet the estimates are for longer periods. Uncommon numerical models are utilized to modify follow atmospheric gases (carbon dioxide and methane, for instance), ocean ice and icy mass cover, changes in approaching sun based radiation, and a large group of different parameters. A numerical portrayal of the atmosphere framework deals in light of the physical, synthetic and organic properties of its parts, their connections and criticism procedures, and representing all or a portion of its known properties. The atmosphere framework can be spoken to by models of shifting multifaceted nature, that is, for any one segment or blend of parts a range or chain of importance of models can be recognized, varying in such angles as the quantity of spatial measurements, the degree to which physical, synthetic or organic procedures are expressly spoken to, or the level at which exact parameterizations are included.
3. Climatology
Climatology is imperative since it explains the future climatic expectations. Using scope, one can decide the probability of snow and hail achieving the surface. You can likewise have the capacity to distinguish the warm vitality from the sun that is open to a locale. Climatology is the logical investigation of atmospheres, which is characterized as the mean climate conditions over some undefined time frame. A branch of concentrate inside climatic sciences, it likewise considers the factors and midpoints of here and now and long-haul climate conditions. Climatology is not quite the same as meteorology and can be isolated into various regions of study. Different ways to deal with this field can be taken, including paleoclimatology, which centers on the atmosphere through the span of the Earth's presence by analyzing records of tree rings, shakes and silt, and ice centers. Chronicled climatology centers basically around atmosphere changes all through history and the impacts of the atmosphere on individuals and occasions after some time.
4. Global Environmental Change
Most climate scientists agree the main cause of the current global warming trend is human expansion of the "greenhouse effect"1 — warming those results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space. Human activities are changing the natural greenhouse. Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). Global warming is primarily a problem of too much carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere—which acts as a blanket, trapping heat and warming the planet.
- Global Warming and its Impacts
- Carbon Emission Sources and Control
- Carbon Discharge Reduction
- Ozone layer depletion
- Carbon capture and storage
- Biofuels
- Integrated ecosystems management
- Satellite applications in the environment
- Environmental restoration and ecological engineering
- Habitat reconstruction
- Biodiversity conservation
- Deforestation
5. Indications of Climate Change
The Earth's atmosphere is evolving. Temperatures are rising, snow and precipitation designs are moving, and more outrageous atmosphere occasions – like substantial rainstorms and record high temperatures – are now happening. A considerable lot of these watched changes are connected to the rising levels of carbon dioxide and other ozone harming substances in our climate, caused by human exercises. Atmosphere researchers are 95 percent sure that the ozone depleting substance discharges from human exercises are making the environmental change. From 1901-2012, temperatures have risen 1.6°F. While this temperature change is the most normally referred to environmental change pointer, there are various others that additionally indicate what environmental change resembles. They run from rising oceans to liquefying icy masses and ice sheets to evolving ecosystem.
6. Co2 as a Major Cause
Environmental change is principally an issue of an excessive amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air. This carbon over-burden is caused primarily when we consume petroleum derivatives like coal, oil and gas or chop down and consume timberlands. There are numerous warmth catching gases (from methane to water vapor), yet CO2 puts us at the most danger of irreversible changes if it keeps on aggregating unabated in the air. People have expanded climatic CO2 fixation by in excess of a third since the Industrial Revolution started. This is the most imperative driving of environmental change. It retains less warmth per particle than the ozone depleting substances methane or nitrous oxide, yet it's more copious and it remains in the environment any longer. And keeping in mind that carbon dioxide is less plentiful and less capable than water vapor on a particle for each atom premise, it ingests wavelengths of warm vitality that water vapor does not, which implies it adds to the nursery impact remarkably.
7. Pollution and its Effects
Air pollution and climate change are firmly related. The fundamental sources of CO2 emissions – the extraction and copying of petroleum derivatives – are key drivers of environmental change, as well as significant wellsprings of air poisons. Moreover, numerous air toxins that are hurtful to human wellbeing and biological systems likewise add to environmental change by influencing the measure of approaching daylight that is reflected or consumed by the air, with a few poisons warming and others cooling the Earth. These short-lived climate-forcing pollutants (SLCPs) incorporate methane, dark carbon, ground-level ozone, and sulfate pressurized canned products. They affect the atmosphere; dark carbon and methane specifically are among the best supporters of a dangerous global warming after CO2.
8. Ecology and Climate Forcing
Ecology is the scientific study of the interactions that govern organism distribution and abundance. The primary goals of natural resource management are to predict and maintain or change the distribution and abundance of various organisms; thus, effective management of natural ecosystems is dependent on ecological knowledge.
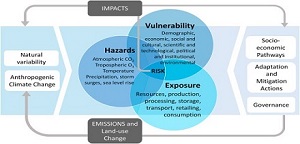
Climate forcing is the physical process of influencing the Earth's climate through a variety of forcing factors. These factors are referred to as forcing because they cause the climate to change, and it is important to note that these forcing exist independently of the existing climate system. The hydrosphere, land surface, cryosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere comprise the climate system. Examples of some of the most important types of forcing include variations in solar radiation levels, volcanic eruptions, changing albedo, and changing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Each of these are considered external forcing because these events change independently of the climate, perhaps as a result of changes in solar activity or human-caused fossil fuel combustion.
9. Ecosystem Assessment & Restoration
The process of assisting in the recovery of ecosystems that have been damaged, destroyed, or degraded is known as ecosystem assessment and restoration. It focuses on establishing the ecological processes required to make terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems sustainable, resilient, and healthy under the circumstances of the present and the future. The goals and strategies used in various restoration projects to accomplish those goals vary. Another goal of many restoration projects is to create or improve ecosystem functions like pollination or erosion control. Many restoration projects aim to create ecosystems made up of native species.
- Nutrients and Functions of Ecosystems
- Restoration of Ecosystems
- Urban Ecology
- Eco-technology
10. Action on climate and SDGS
The availability of necessities like freshwater, food security, and energy are expected to be affected for many people by a warming climate system, while efforts to address climate change, through both adaptation and mitigation, will similarly inform and shape the global development agenda. There are strong connections between climate change and sustainable development. The least developed and underdeveloped nations will be among those most negatively impacted and least equipped to deal with the expected shocks to their social, economic, and environmental systems. The associated targets of the sustainable development goal are more specifically focused on integrating climate change measures into national policies, as well as improving institutional capacity for early warnings, impact reduction, mitigation, and awareness-raising.
11. Climate Technologies
Information on innovation, research, and development in the fields of environmental science, energy resources and processes, cutting-edge technologies, and energy efficiency can be found in the journal Environmental and Climate Technologies. Authors are encouraged to submit manuscripts that address a wide range of subjects, including resilience, building energy efficiency, secure and sustainable energy sources, life cycle analysis, eco-design, climate change mitigation, and innovative pollution reduction solutions. Original research and creative work are given international exposure thanks to the Journal. A multi-disciplinary approach that incorporates all facets of environmental science covers a wide range of topics:
- Sustainability of technology development
- Bioeconomy
- Cleaner production, end of pipe production
- Zero emission technologies
- Eco-design
- Life cycle analysis
Market Analysis
Market Overview:
Climate change will be one of the most economically impactful events in human history. But currently, our profession is in many cases behind the curve in analyzing the impacts of Climate change. This report from CFA Institute includes case studies and survey data to help educate our community and investors about what Climate change is and its economic impacts, best practices in analysis, and where to find information for integrating Climate change in the investment process.
Estimates of the costs of Climate change have a wide range, but they are all bad. A recent report by the Economist Intelligence Unit estimated the net present value costs of Climate change at US$4.2 trillion.
The cost of adapting to Climate change in developing countries could rise to between $280 and $500 billion per year by 2050, a figure that is four to five times greater than previous estimates, according to a new United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) report. The Fourth National Climate Assessment published in 2018 by the US Global Change Research Program states, “Without substantial and sustained global mitigation and regional adaptation efforts, Climate change is expected to cause growing losses to American infrastructure and property and impede the rate of economic growth over this century.”
Climate change is a force that is already impacting economies and financial market.
s and, due to the nature of the problem, can be expected to do so with more frequency in the near future. Today, financial professionals have few tools for including Climate change metrics in their financial models.
This report focuses on the issue of Climate change to help our community and all financial professionals to better integrate climate analysis into their investment process. The report also contains a global survey of CFA Institute participants to gauge their understanding of the issue and includes case studies that can help teach investors how to integrate Climate change analysis into the investment process.
Key Tools for Climate Analysis in Investing:
As the earth’s atmosphere warms and the side effects of Climate change become more prevalent, more pressure will be placed on everyone, including financial professionals, to take actions that address Climate change. To do this important work, financial professionals need a few key tools.
• A price on carbon — CFA Institute calls on policymakers to ensure that regulatory frameworks for carbon markets are designed to deliver transparency, liquidity, ease of access for global market participants, and similar standards across jurisdictions, in order to underpin robust and reliable carbon pricing.
• Carbon price expectations included in analyst reports — CFA Institute recommends that investment professionals account for carbon prices and their expectations thereof in climate risk analysis.
• Increased transparency and disclosure on climate metrics — CFA Institute acknowledges that the investment industry is coalescing around the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) and Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) standards for climate-related disclosures, which are the most relevant and succinct climate-related disclosure standards for addressing the materiality of climate-related risks.
• Engagement with companies on physical and transition risks of Climate change — we believe investors should engage with issuers to ensure that climate data, scenario analysis, and related disclosures are sufficiently thorough to support robust climate risk analysis in the investment process.
• Education within our profession — Investors need to continue to educate themselves about Climate change in order to provide clients with the climate-related analysis they deserve.
• Policy that complements our efforts — Investors need to continue to meet with policymakers in order to make sure that investors have the tools they need to do the work of finance — that is, the efficient allocation of capital that helps to tackle the existential threat of Climate change.
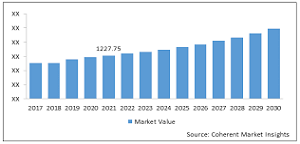
Economic and Market Implications of Climate change:
Investors need to educate themselves on the economics of Climate change and understand the implications of a heating world on their investments. As we explore in the next section, this includes understanding the risks as well as opportunities that may arise. To perform this analysis, investors need better data and better reporting standards around climate-related data. They should therefore engage with corporate issuers and policymakers to help inform best practices and standards for Climate change–related disclosures.
Physical Risks, Transition Risks, and Opportunities:
Investors need to understand how the physical and transition risks brought on by Climate change will affect the companies in which they invest. Some of these risks are slowly growing threats, and others have already emerged. Investors should understand the expected intensity or frequency of such risks when possible and engage with companies to understand what strategic steps each company has or has not taken to mitigate these risks. At the same time, the immense changes in society brought about by a Climate change transition will present opportunities to investors in both established and nascent industries.
A Price on Carbon: Carbon Markets:
Investors should educate themselves about how carbon markets work in order to better incorporate a likely higher price on carbon into their analysis. Analysts and portfolio managers should run their own scenario analysis to better understand how a carbon price of US$50–US$100/tCO2 in 2030, as recommended by the Stern–Stiglitz Report of the High-Level Commission on Carbon Prices, would affect the companies they analyse or hold in their portfolios. CFA Institute recommends analysts begin factoring expected carbon prices into their financial analysis so they can be prepared for a world with more explicit carbon pricing, whatever form those prices take. See the case study “Carbon as an Emerging Asset Class” for a more in-depth look at the issue of carbon pricing and carbon markets.
Scenario Analysis:
Scenario analysis offers investors a tool to imagine a number of different Climate change scenarios based on their own research and understanding of the probabilities of certain outcomes. Investors should engage with companies to include more scenario analysis in company disclosures to help investors better understand the possibilities a company faces concerning certain climate-related issues.
Global Climate change Consulting Market- Impact of Coronavirus (Covid-19) Pandemic:
The rapid outbreak of COVID-19 across the globe has significantly affected all industries globally. The situation caused significant deterioration in economic conditions and the government had to shut down commercial as well as educational sectors for a specific period. Strict containment measures have resulted in a drop of economic activities, the business environment of many organizations has changed. For instance, the on-going and planned projects of construction, mining, and other industries have been delayed, or cancelled. Due to lockdown, projects consulting projects were either postponed or cancelled which impacted the business of consulting service providers.
On the other hand, COVID-19 has brought about short-term environmental benefits as a temporary reduction in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases, as people were forced to stay at home and industries such as mining, construction, and textiles remained closed for a period.
Key features of the study:
- This report provides an in-depth analysis of global Climate change consulting market size (US$ Billion) and compound annual growth rate (CAGR %) for the forecast period (2022 to 2030), considering 2021 as the base year.
- It elucidates potential revenue opportunities across different segments and explains attractive investment proposition matrices for this market.
- This study also provides key insights about market drivers, restraints, opportunities, new product launches or approvals, regional outlook, and competitive strategies adopted by the leading market players.
- It profiles leading players in the global Climate change consulting market based on the following parameters – company overview, financial performance, product portfolio, geographical presence, market capital, key developments, strategies, and future plans.
- Consultancy companies covered as a part of this study include ICF International, Inc., A.T. Kearney, Inc., McKinsey & Company, Inc., PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (PwC), ERM Group, Inc., KPMG International, Coastal Risk Consulting, LLC, CH2M HILL Companies, Ltd. (Jacobs Engineering Group), Deloitte LLP, Ramboll Environ, Inc.
- Insights from this report would allow marketers and management authorities of companies to make informed decisions regarding future product launches, product upgrades, market expansion, and marketing tactics.
- The global Climate change consulting market report caters to various stakeholders in this industry including investors, suppliers, managed service providers, third-party service providers, distributors, new entrants, and value-added resellers.
- Stakeholders would have ease in decision-making through various strategy matrices used in analyzing the global Climate change consulting market.
Global Climate change Consulting Market, By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
- Green Building Services
Global Climate change Consulting Market, By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)

Global Climate change Consulting Market, By Region:
North America:
By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)
By Country:
Europe:
By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)
By Country:
Asia Pacific:
By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)
By Country:
Latin America:
By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)
By Country:
Middle East and Africa:
By Service Type:
- Corporate Strategy for Climate change
- Carbon Footprint Analysis, Emission Trading and Offsetting
- Renewable Energy Development
- Energy Efficiency
- Policy and Economics
- Climate Adaptation Analysis & Planning
By Industry:
- Mining
- Energy & Utilities
- Government
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others (Construction, Agriculture, Forestry, etc.)
By Region:















